Introduction
Blockchain networks are not immune to threats. In 2024 alone, on-chain exploits cost the industry over $2.3 billion. Traditional security tools simply cannot keep pace. The speed of decentralized transactions demands something faster and smarter. This is where real-time blockchain threat monitoring becomes mission-critical. Unlike reactive audits, real-time anomaly detection watches every block, every transaction, and every contract interaction as it happens. This advanced guide breaks down the architectures, detection models, and operational strategies that security engineers use to defend live blockchain environments. If you build or secure Web3 infrastructure, this is your playbook.
Why Real-Time Detection Changes Everything
Post-incident forensics tell you what happened. Real-time blockchain threat monitoring tells you what is happening right now. The median time between exploit initiation and fund drainage is under four minutes. Blocks confirm every 12 seconds on Ethereum. That window is brutally narrow.
Traditional SIEM tools work with log files and API delays. They were not built for mempool data or on-chain event streams. Real-time systems must ingest raw node data, parse bytecode, and fire alerts within milliseconds. The financial and reputational cost of a single missed alert is enormous. Real-time systems do not just detect threats they buy you the seconds needed to respond.
Architecture of a Real-Time Blockchain Monitoring System
Building a robust monitoring pipeline requires four layered components working in concert.
1. Data Ingestion Layer
Your monitoring stack lives or dies at ingestion. You need full-node WebSocket subscriptions for pending transactions, confirmed block data, and event log emissions simultaneously.
Tools commonly used at this layer include: Ethereum’s eth_subscribe for newPendingTransactions, Infura or Alchemy webhooks for confirmed events, and custom Geth or Erigon archive nodes for historical baselines.
2. Stream Processing Layer
Raw transaction data must be decoded, enriched, and classified in near-zero latency. Apache Kafka or AWS Kinesis handles high-throughput event streaming at this layer.
Decoding ABIs, resolving token addresses, and mapping wallet histories all happen here. The output feeds both anomaly detection models and the alerting engine downstream.
3. Detection Engine
This is the intelligence core. It runs both rule-based and ML-based models concurrently. Rules catch known attack signatures instantly. Models catch novel deviations statistically.
4. Alerting and Response Layer
Alerts must be actionable, not just informational. A well-designed alerting layer routes threat severity to the right channel PagerDuty for P0 events, Slack for P2 anomalies, dashboards for trends.
Automated response playbooks such as pausing a vulnerable contract via a guardian wallet can be triggered directly from this layer, cutting human latency out of the loop.
Advanced Anomaly Detection Techniques for Blockchain
No single model catches everything. Advanced real-time blockchain threat monitoring stacks multiple complementary techniques.
Statistical Baseline Deviation Models
Every contract builds a behavioral fingerprint over time average gas usage, call frequency, value throughput, and unique caller distribution. Statistical models establish rolling baselines from this data.
Z-score analysis and Exponentially Weighted Moving Averages (EWMA) are particularly effective. A flash loan attack, for example, shows a massive single-block value spike a clear statistical outlier against any normal baseline.
Graph-Based Transaction Analysis
Blockchains are fundamentally transaction graphs. Addresses are nodes; value transfers are directed edges. Graph anomaly detection looks for suspicious structural patterns within this web. Patterns like rapid fan-out from a single wallet, circular fund flows between controlled addresses, and sudden clustering around mixer contracts are detectable via graph traversal algorithms at scale. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are increasingly used here. They learn embedding representations of wallet behavior and flag wallets whose graph neighborhood suddenly changes topology.
Machine Learning–Based Anomaly Detection
Unsupervised models like Isolation Forest and Autoencoders are ideal for blockchain anomaly detection because labeled attack datasets are limited and attackers constantly innovate. Isolation Forest identifies anomalies by measuring how easily a data point can be separated from the rest of the dataset. A re-entrancy exploit mid-transaction shows dramatically different call stack depth an Isolation Forest flags this fast. LSTM-based sequence models track temporal transaction patterns. They learn the normal rhythm of DeFi protocol usage and raise alerts when sequences deviate from learned norms.
Bytecode and Opcode Analysis
Smart contract bytecode tells a story before deployment. Opcode-level analysis can identify dangerous patterns delegate call into user-controlled addresses, unchecked external calls, and self destruct in unguarded code paths. Newly deployed contracts with suspicious opcode signatures trigger immediate elevated scrutiny. Monitoring systems can compare new bytecode against a library of known exploit contracts using fuzzy hashing techniques like TLSH.
Key Blockchain Threat Patterns to Monitor in Real Time
Real-time blockchain threat monitoring must target the highest-impact attack vectors first. These are the patterns that cause the most damage.
- Flash Loan Attacks: Watch for single-block multi-protocol interactions exceeding abnormal value thresholds from unfunded wallets.
- Re-Entrancy Exploits: Monitor recursive external call patterns and unexpected state change sequences within a single transaction.
- Oracle Manipulation: Detect sharp price deviations between on-chain oracle feeds and aggregated off-chain market data.
- Governance Attacks: Alert on abnormal token accumulation spikes before proposal submission windows.
- Front-Running and MEV Extraction: Identify sandwich attack patterns via mempool transaction ordering analysis.
Each of these attack types leaves a detectable signature. The challenge is catching them in the sub-second window before irreversible state changes finalize on-chain.
How SecuredApp Enables Advanced Real-Time Threat Monitoring
Building a full real-time monitoring stack from scratch demands enormous engineering investment. SecureDApp was built to provide this infrastructure out of the box for Web3 security teams. SecureDApp’s on-chain monitoring suite delivers continuous smart contract surveillance across EVM-compatible chains. It ingests live transaction data, applies behavioral baselines, and surfaces anomalies with context-rich alerts all without requiring you to manage your own node infrastructure.
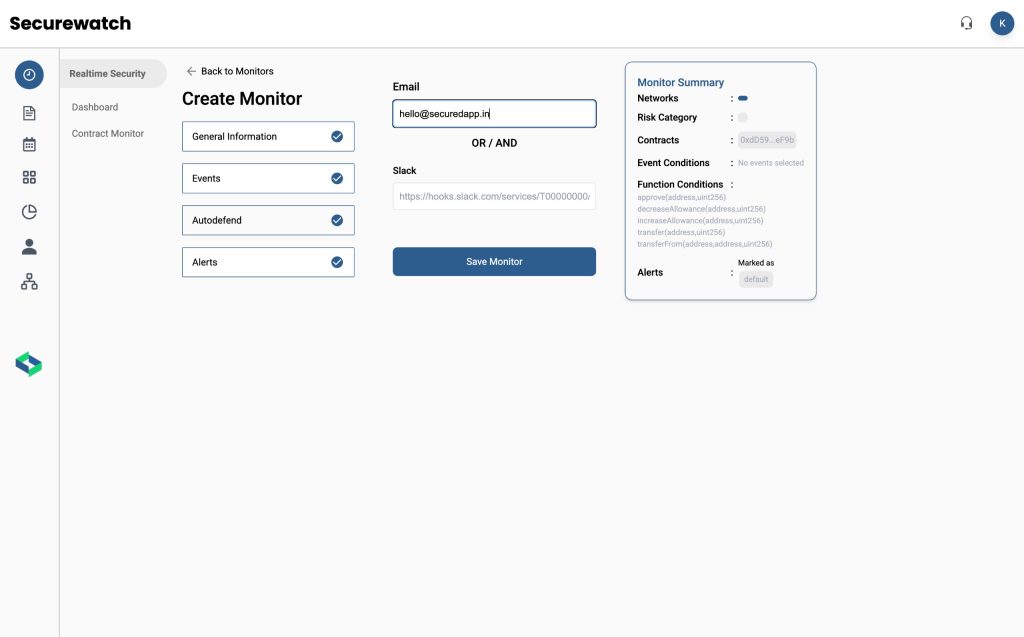
The platform also integrates smart contract audit capabilities, meaning security posture assessment and live threat monitoring work from the same unified context. Audit findings feed directly into monitoring rule templates, so known vulnerabilities in your contracts get watched most closely. For teams that need bug bounty programs alongside active monitoring, SecureDApp provides an integrated workflow. This closes the loop between external researcher findings and internal monitoring coverage.
Reducing False Positives Without Sacrificing Coverage
Alert fatigue kills security programs. If every notification is a false positive, engineers stop responding. Precision matters as much as recall. Several techniques sharpen signal quality in blockchain monitoring environments without reducing true-positive capture rates.
Contextual Enrichment Before Alerting
Never alert on raw transaction data alone. Enrich every flagged event with historical wallet behavior, known protocol context, and token-level metadata before routing to an alert queue.
A large value transfer from a known institutional custodian wallet is normal. The same transfer from a newly funded wallet created 48 hours ago is critical. Context transforms noise into signal.
Multi-Signal Confirmation Thresholds
Require two or more independent signals to fire a P0 alert. For example: a statistical spike AND a new wallet AND an unusual call pattern together. Each alone may be noise; together, they indicate a credible threat.
Adaptive Baseline Tuning
Protocol usage patterns shift. A token launch, governance vote, or DeFi incentive program creates legitimate activity spikes. Monitoring systems must adapt baselines dynamically during known high-activity events.
Scheduled baseline recalibration windows and event-triggered threshold adjustments prevent protocol-level activity from overwhelming alert queues with false positives.
Cross-Chain Monitoring Challenges and Solutions
Modern DeFi attacks routinely span multiple chains. An exploit may begin on Ethereum, bridge funds to Arbitrum, swap on Polygon, and exit through a BSC mixer all within minutes.
Siloed per-chain monitoring misses this attack surface entirely. True cross-chain real-time blockchain threat monitoring requires a unified identity layer that correlates addresses across chains via bridge contracts, common deployer wallets, and shared infrastructure fingerprints.
Bridge contract events are especially high-value monitoring targets. They represent the transition points where assets move between trust boundaries. Monitoring DepositInitiated, MessagePassed, and RelayedMessage events across major bridges catches cross-chain fund movements in real time.
Integrating Monitoring with Incident Response Playbooks

Detection without response is observation, not security. Every high-severity alert must map to a pre-defined incident response playbook. For smart contracts with guardian or pause mechanisms, automated response systems can call the pause function directly from the monitoring platform when a threshold attack pattern is confirmed. This eliminates human latency from the most critical response window.
For lower-severity events, documented playbooks should specify exactly what analyst actions follow each alert type. Consistent response reduces decision fatigue and prevents errors under pressure. Post-incident reviews must feed back into the detection system. Every confirmed exploit that bypassed monitoring reveals a gap. Closing that gap makes the system stronger for the next attack cycle.
Measuring the Effectiveness of Your Monitoring System
You cannot improve what you do not measure. Quantitative metrics keep real-time blockchain threat monitoring programs accountable and guide improvement investment.
- Mean Time to Detect (MTTD): How long from exploit initiation to first alert? Target under 30 seconds for on-chain events.
- False Positive Rate (FPR): Track weekly. High FPR indicates baseline or model tuning is needed urgently.
- Alert Coverage Ratio: What percentage of your contract’s attack surface is covered by active monitoring rules?
- Response Time: Measure time from alert generation to first analyst action for each severity tier.
- Model Drift Rate: How frequently do ML model accuracy metrics degrade, requiring recalibration cycles?
Review these metrics in weekly security operations cadences. Trend analysis over 30, 60, and 90-day rolling windows reveals systemic gaps that point-in-time reviews miss.
Conclusion: Detection Speed Is a Competitive Advantage
The blockchain threat landscape is sophisticated, fast-moving, and unforgiving. Post-incident audits are valuable for learning. Only real-time blockchain threat monitoring gives you a chance to act before damage becomes permanent. The advanced techniques covered in this guide from statistical baselines and graph neural networks to cross-chain correlation and automated incident response represent the current state of the art in blockchain anomaly detection. Implementing even a subset of these approaches dramatically raises the cost and complexity for attackers targeting your protocol. Combined with proactive security auditing and an active bug bounty program through SecureDApp, you create defense-in-depth that protects assets, reputation, and user trust.
FAQs
A: It is the continuous surveillance of on-chain activity transactions, contract events, and wallet behaviors to detect malicious or anomalous patterns instantly as they occur on the network.
A: Blockchain monitoring operates on immutable, public transaction data with sub-second confirmation windows. Traditional SIEM tools rely on log files and API integrations that cannot match blockchain’s throughput or decentralized architecture.
A: Monitoring can detect flash loan attack patterns in the mempool or within confirmed blocks and trigger automated responses. However, prevention requires architectural safeguards like circuit breakers and oracle time-weighted averages built into the contract itself.
A: Enterprise-grade solutions like SecureDApp support all major EVM-compatible chains including Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, BNB Chain, and Avalanche, with cross-chain correlation across supported networks.
A: Rule sets should be reviewed and updated monthly at minimum, and after every major industry exploit. ML models should be evaluated for drift quarterly, with full retraining cycles whenever accuracy metrics decline beyond defined thresholds.



